Ankle Arthroscopy: A Minimally Invasive Solution
Ankle arthroscopy is a cutting-edge surgical technique that has revolutionized the treatment of various ankle joint conditions. Unlike traditional open surgery, which often involves larger incisions and more prolonged recovery times, ankle arthroscopy is minimally invasive, offering patients the advantages of smaller incisions, less pain, and quicker recovery.
This procedure utilizes a tiny camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments to diagnose and treat a wide range of ankle issues, making it a popular choice among patients and orthopedic surgeons alike. In this article, we will explore ankle arthroscopy in detail, its indications, the surgical process, and what patients can expect during recovery.
Understanding the Ankle Joint
The ankle is a complex joint that plays a critical role in mobility and balance. It is composed of three bones: the tibia (shinbone), fibula (calf bone), and talus (the top of the foot bone). The joint is stabilized by ligaments and surrounded by a joint capsule filled with synovial fluid. Thus, any disruption to the normal function of the ankle joint can result in pain, limited range of motion, and reduced quality of life.
Indications for Ankle Arthroscopy
Ankle arthroscopy is recommended for a variety of ankle conditions, including:
Ankle Impingement: This occurs when excess bone or soft tissue in the joint causes pain and restricted movement.
Synovitis: Inflammation of the synovial lining in the joint can lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Osteochondral Lesions: These are defects in the cartilage and underlying bone in the ankle joint, often caused by injury or wear and tear.
Ankle Ligament Tears: Chronic instability and recurrent sprains may require repair or reconstruction of damaged ligaments.
Foreign Body Removal: Ankle arthroscopy can be used to remove loose bodies or debris from the joint.
Cartilage Damage: The procedure can address cartilage injuries, helping to alleviate pain and prevent further deterioration.
The Ankle Arthroscopy Procedure
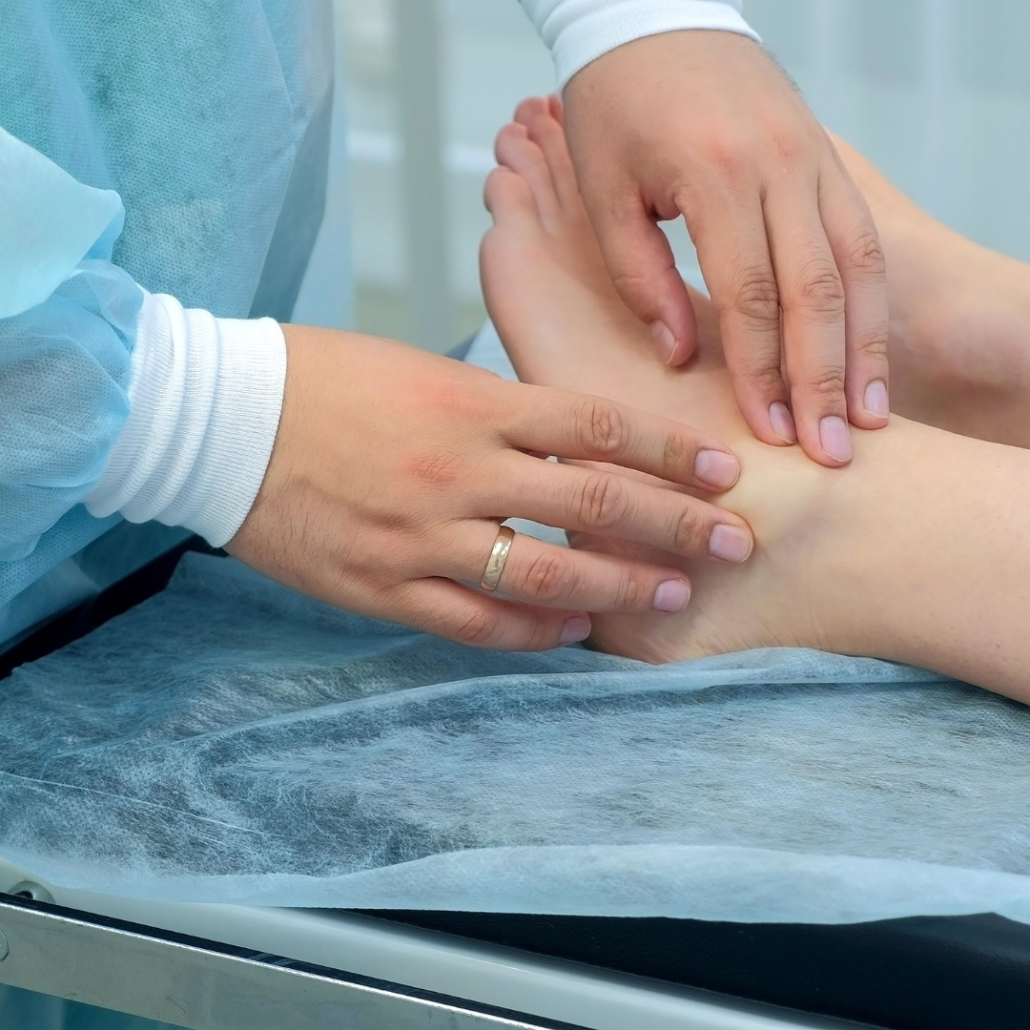
Ankle arthroscopy typically takes place as an outpatient procedure under local or general anesthesia. Here’s a step-by-step overview of the surgical process:
Step 1: Preparation
The patient is positioned on the operating table, and the ankle is thoroughly cleaned and sterilized. The surgeon may inflate a tourniquet on the upper thigh to limit blood flow to the surgical area, enhancing visibility and reducing bleeding during the procedure.
Step 2: Incisions
The surgeon makes a few small incisions around the ankle joint, usually no more than 5 millimeters in size. These incisions serve as portals for the arthroscope and surgical instruments.
Step 3: Arthroscopy
The arthroscope, a thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera attached to the end, is inserted through one of the incisions. Thus, the camera transmits high-definition images of the inside of the ankle joint to a monitor in the operating room, allowing the surgeon to visualize the joint’s structures in real-time.
Step 4: Diagnosis and Treatment
Based on the arthroscopic findings, the surgeon can diagnose the specific problem within the ankle joint. As a result, if a treatment is essential, the insertion of instruments of specialisation happens through the other incisions to perform the necessary repairs.
For ankle impingement, the surgeon can remove excess bone or soft tissue causing the impingement.
- In cases of synovitis, inflamed tissue is easily removable.
- Osteochondral lesions is treatable by removing damaged tissue or drilling small holes to stimulate the growth of healthy cartilage.
- Ankle ligament tears may require repair or reconstruction using sutures or grafts.
- The removal of loose bodies or debris takes place from the joint.
- The addressing of cartilage damage is neccesary for procedures like microfracture or chondroplasty.
Step 5: Closure
After the necessary repairs are good to go, the removal of instruments and arthroscope happens, and they close the incisions with sutures or adhesive strips. A sterile dressing takes place on the ankle.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery following ankle arthroscopy is typically quicker and less painful compared to traditional open surgery. Patients can often bear weight on the affected ankle shortly after the procedure, depending on the extent of the surgery and the surgeon’s recommendations.
Rehabilitation is a crucial aspect of the recovery process. Physical therapy helps improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the ankle. The specific rehabilitation plan varies depending on the condition treated and the patient’s individual needs.
Patients may require crutches or a brace for a short period to support the ankle while it heals. That is why, it’s essential to follow the surgeon’s post-operative instructions carefully to ensure a successful recovery.
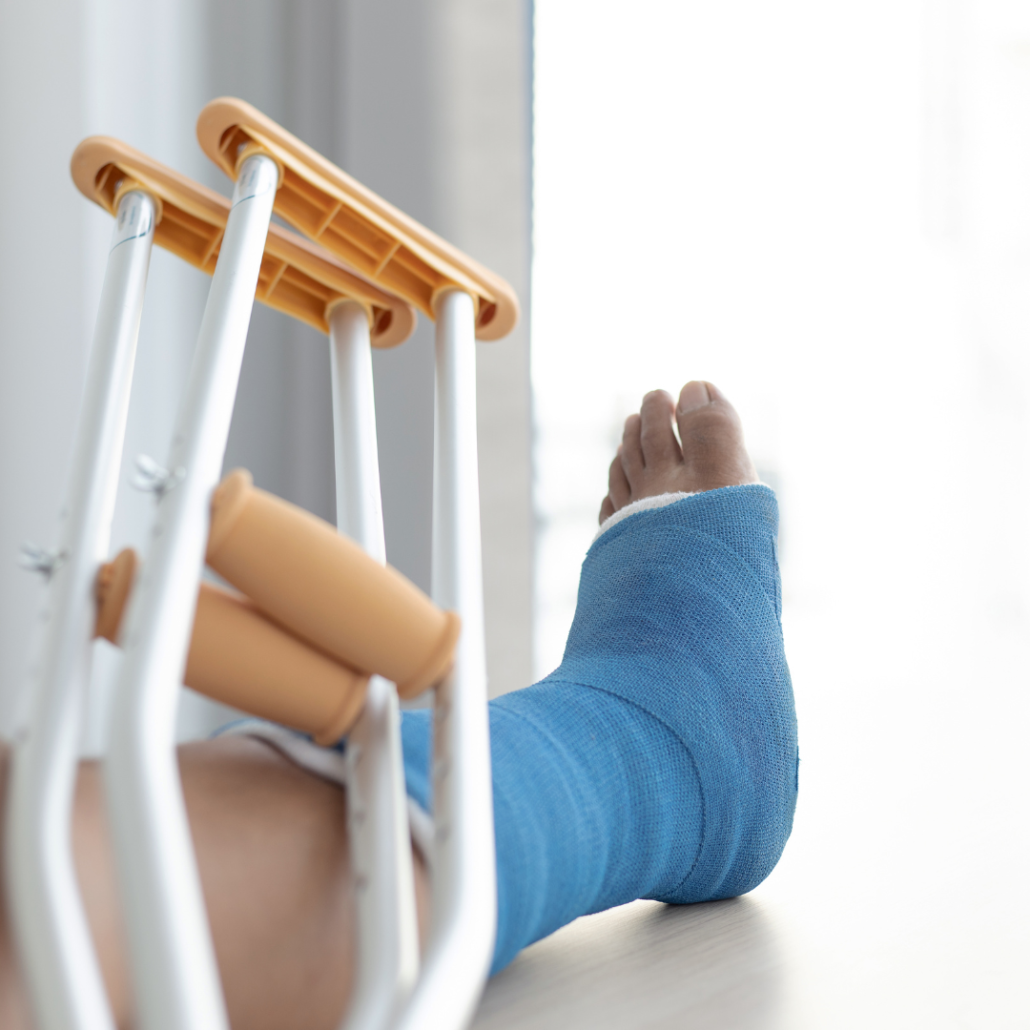
Advantages of Ankle Arthroscopy
Ankle arthroscopy offers several advantages over traditional open surgery:
Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions result in less tissue damage, reduced scarring, and a lower risk of infection.
Faster Recovery: Patients typically experience less pain and can return to daily activities sooner than with open surgery.
Accurate Diagnosis: The arthroscope provides real-time visualization of the joint, allowing for precise diagnosis and targeted treatment.
Less Blood Loss: The use of tourniquets and smaller incisions minimizes bleeding during the procedure.
Lower Risk: Overall, ankle arthroscopy carries a lower risk of complications compared to open surgery.
Thus,
Ankle arthroscopy has revolutionized the treatment of various ankle conditions, offering patients a minimally invasive, precise, and effective solution. Whether it’s addressing impingement, synovitis, ligament tears, osteochondral lesions, or cartilage damage, ankle arthroscopy allows orthopedic surgeons to diagnose and treat ankle issues with greater accuracy and less trauma to surrounding tissues.
As technology and techniques continue to advance, ankle arthroscopy remains a valuable tool in restoring ankle function and improving the quality of life for individuals with joint problems. Thus, if you’re experiencing ankle pain or mobility issues, consult with an orthopedic specialist to determine if ankle arthroscopy is the right option for you.












Really clear internet site, regards for this post.
I will immediately grab your rss feed as I can’t find your e-mail subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please let me know in order that I could subscribe. Thanks.
I am extremely impressed with your writing skills and also with the layout on your weblog. Is this a paid theme or did you modify it yourself? Either way keep up the excellent quality writing, it’s rare to see a great blog like this one nowadays..
Good write-up, I?¦m regular visitor of one?¦s site, maintain up the nice operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
Very interesting points you have observed, regards for posting. “My work is a game, a very serious game.” by M. C. Escher.
I’ve recently started a web site, the information you provide on this web site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work. “The more sand that has escaped from the hourglass of our life, the clearer we should see through it.” by Jean Paul.
I rattling thankful to find this web site on bing, just what I was searching for : D as well bookmarked.
Thanks for ones marvelous posting! I really enjoyed reading it, you’re a great author.I will remember to bookmark your blog and may come back down the road. I want to encourage one to continue your great work, have a nice afternoon!
What’s Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to contribute & assist other users like its aided me. Good job.